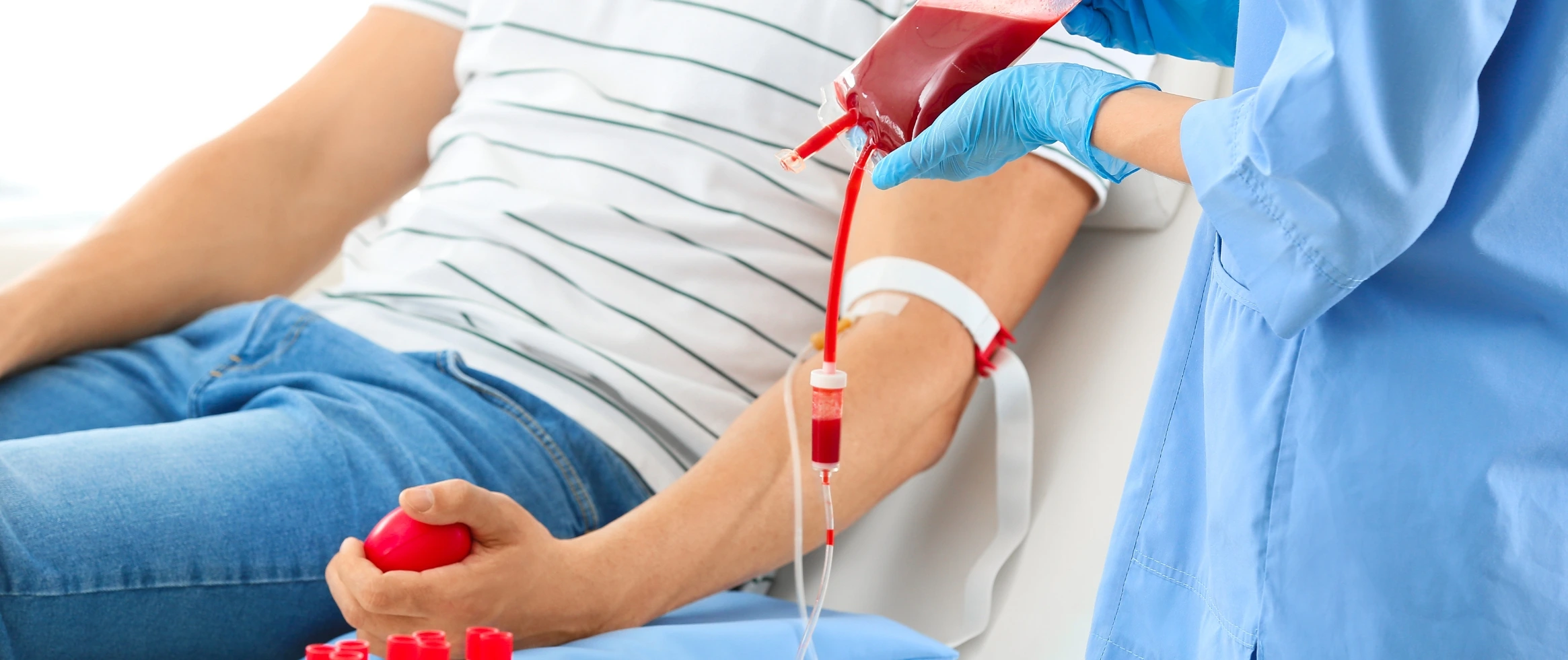
A Complete Blood Count (CBC) is a frequently performed test that checks for diseases impacting your health. The CBC measures three fundamental categories of blood cells: red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. It identifies any changes in your blood cell counts, whether positive or negative.
Normal values vary based on age and gender. By monitoring these levels, your doctor can assess your general health and detect potential illnesses. Regular CBC tests help in early detection and management of health conditions.
What exactly is a CBC?
A simple and frequently performed test called a complete blood count, or CBC is used to check for specific diseases that may have an impact on your health. A CBC identifies any alterations in your blood cell counts, whether positive or negative. Depending on your age and gender, there are different normal values.
Your doctor may be able to assess your general health and identify illnesses by monitoring changes in your blood cell levels. The three fundamental categories of blood cells are measured by the test.
Red blood cells
- Your body receives oxygen via red blood cells, which also eliminate carbon dioxide. Your red blood cells' two constituents are measured by a CBC: A protein that transports oxygen
- The haematocrit test determines how many red blood cells are present in your blood.
- Anaemia, a disorder that develops when blood is iron deficient, is frequently indicated by low levels of haemoglobin and haematocrit.
WBCs are white blood cells
Your body uses white blood cells to fight illness. A complete blood count (CBC) determines the number and type of white blood cells in your body. Any unusual increases or declines in the number or type of white blood cells could indicate infection, inflammation, or malignancy.
Platelets
Platelets aid in the clotting of blood and the control of bleeding. Platelets are responsible for stopping bleeding after a cut. Any variations in platelet levels can put you at risk of excessive bleeding and indicate a dangerous medical problem.
What does the Complete Blood Count (CBC) test evaluate?
A CBC includes several parameters, including the number of blood cells and some of their physical characteristics. A conventional CBC has various elements about RBCs, WBCs, and PLT (platelets), which are explained in the sections that follow.
Measurements of red blood cells
RBCs, commonly known as erythrocytes, transport oxygen from your lungs to your tissues and organs. A CBC test comprises several basic RBC measurements:
- total amount of RBCs in your blood The sample is referred to as the RBC count.
- The amount of this oxygen-carrying protein contained inside RBCs is measured by haemoglobin.
- Haematocrit is the percentage of your total blood volume that is made up of RBCs.
The physical characteristics of RBC are also described in CBC.
- The average size of RBC is determined by the term "mean corpuscular volume" (MCV).
- The average quantity of haemoglobin found inside each RBC is called mean corpuscular haemoglobin (MCH).
- Mean corpuscular haemoglobin concentration (MCHC) is a calculation used to determine how concentrated haemoglobin is within RBC.
- Red cell distribution width (RDW) is a measurement of the size variance in your RBC.
Measurements of white blood cells
Leukocytes, commonly known as white blood cells or WBCs, are a crucial component of the body’s immune system. The total number of WBCs in a sample of blood is measured by the WBC count, which is part of a typical CBC. The CBC with differential is one of the most popular CBC variations. The five different types of WBCs are broken down into the WBC differential as follows:
- Neutrophil
- Lymphocytes
- Monocytes
- Eosinophils
- Basophils
Measurements of platelets
Blood-circulating cell fragments known as platelets (PLT), also known as thrombocytes, are crucial for blood coagulation. The PLT count, or the quantity of PLT in your blood sample, is a regular part of the CBC.
When should one have a full blood count?
The CBC test is extremely common. A CBC may be performed as part of a routine health examination, when you are being diagnosed or evaluated for an illness or condition, or when your physician is evaluating the success of treatment. Because blood counts can be influenced by a wide range of health disorders, your doctor may recommend the CBC to assist pinpoint the origin of a variety of symptoms. Your doctor is the best person to tell you whether a CBC is necessary for your particular situation.
How the test is performed?
During a CBC, a lab worker will draw blood from a vein, typically on the inside of your elbow or the back of your hand. It will not take long for the test to finish. the technologist
- Using an antiseptic wipe your skin is cleansed
- An elastic band or tourniquet is put around your upper arm to give pressure on the vein to swell with blood
- A needle is inserted to draw the blood from the vein into one or more containers.
- Then the elastic band is taken off, and the region is bandaged to stop any bleeding.
- Later, your sample is sent to a lab for analysis after labelling it.
Test Results of Complete Blood Count (CBC)
The normal levels
Red blood cells:
4.5 million to 5.9 million cells/mcL in males
4.1 million to 5.1 million cells/mcL in females
For haemoglobin:
Male (15+ years old): 13.0–17.0 g/dL
Female (over 15 years old): 11.5–15.5 g/dL
For Haematocrit:
Male: 40 - 55%
Feminine: 36 to 48%
For platelet count: Adult: 150,000-400,000/mL
White blood cell (WBC): 5,000–10,000/mL for adults
Abnormal levels
- Anaemia, heart disease, or a deficiency in iron in the body can all be indicated by abnormally high or low quantities of red blood cells, haemoglobin, or haematocrit.
- A low white cell count could indicate malignancy, autoimmune disease, or bone marrow problems.
- A high white cell count could indicate an illness or a drug reaction.



 NABL approved
NABL approved  Most Trusted by
Most Trusted by  Accuracy &
Accuracy &  Widest Range
Widest Range 



















.jpg)












































.webp)










































































.webp)








.webp)






























21042506111174.webp)


















22052506503962.webp)


26052506100124.webp)
26052506290174.webp)










_Meaning,Causes,andTreatmentOptions25062503385408.webp)